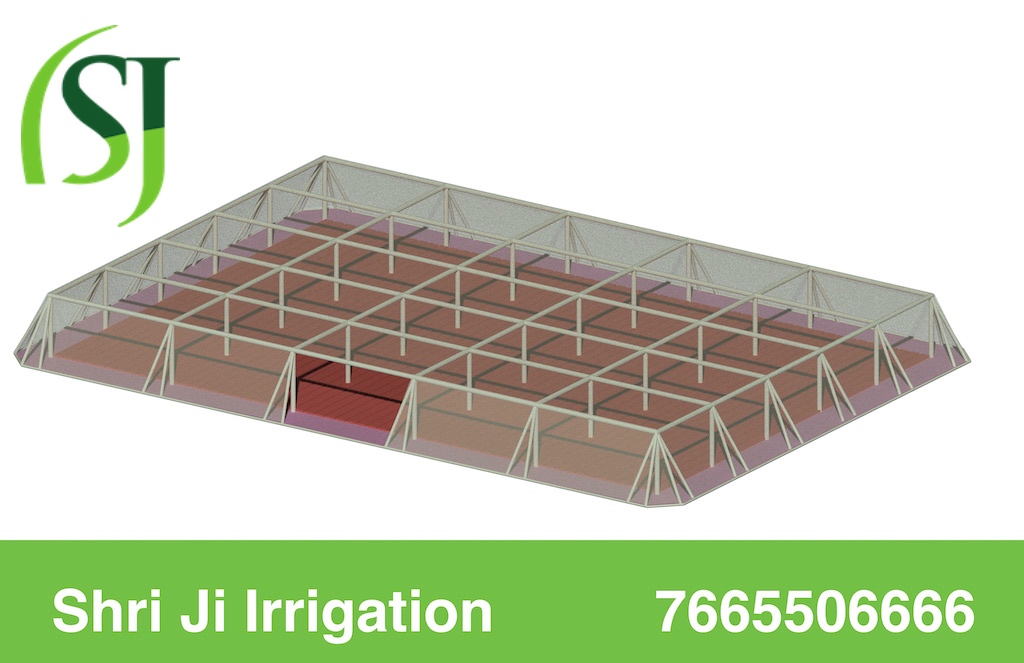
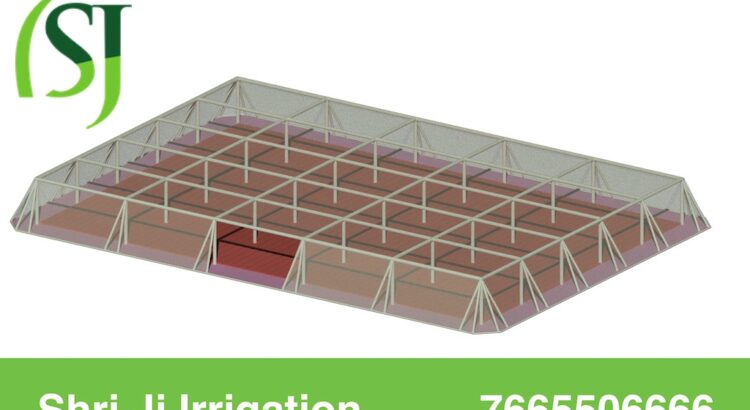
Shade Net House are the superior quality which is efficient enough to maintain the optimum temperature and humidity required for the growth of the planted saplings and crops. Our offered net houses are very long lasting and they have the ability to provide the required sunlight and shade even in very hot summers and cold winters.
What is net house farming and what are its benefits?
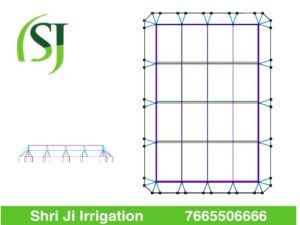
The shade net house is a structure of GI pipe which is tightened with the help of nuts and bolts, in which we install the shade net in the top and the insect net on the side with the help of the profile and spring, it does not come out very close to the outside. So, while installing net house helps us to control tempter and humidity.
So that the crop in the net house can be protected from insects and can prevent the crop from getting spoiled by the direct sunlight.
How do I build a net house?
To make a net house, you should use GI pipe and cut 1 meters from it and with the help of cement, sand, ballast, put it inside the soil, you can make all the pipes standing by making the pipe length of 4 meters. Please give it, as soon as all the pipes are standing, then you put a profile in it.
With the help of SDS screw, your net house complete is ready and when you fix the shade on net house with the help of net profile and spring, we will call it Shade Net House. Written in the Image.
What is shadenet?
The Shade net is a net made of a HDPE material, in which we get shade to protect the plants from the sun, it is called the Shade net house.
Shade Net For Poly House
Shade Net For Poly House is also used in green house & nethouse.
Pests and insects cause immense damage to the yield by feeding on or sucking the plant, depositing eggs on the crop and spreading disease.
How do the Nets Work?
- Nethouses: Light Weight frames with poles and cables that support the net.
- Greenhouses: Air Vents are covered with nets, or all the greenhouse walls are made of nets.
- Walk-in Tunnels: completely covered with net, or covered with net and PE sheets.
- OptiNet is a sophisticated new-generation anti-insect net that integrates physical and optical protection.
Anti Insect Nets:
- 17-mesh net: For protection against fruit files (Mediterranean fruit fly and Fig fruit fly) in orchards and vineyards,Grape moth and Pomegranate Deudorix livia.
- 25-mesh net: For protection against mediterranean fruit fly in peppers.
- 40-mest net: For partial blocking of white flies where climatic conditions do not allow the use of 50 mesh nets.
polyester netting which has insecticide bound to the external surface of the netting fibre using a resin; polyethylene which has insecticide incorporated into the fibre and polypropylene which has insecticide incorporated into the fibre.
These nets come with a guarantee of 5 Years against UV degradation.
Feature
Shade Net house – Better Quality of Produce, Higher Productivity, Nursery Raising & Hardening of Plants, Better insect & disease control & reduced use of pesticides, Off-season Cultivation, Efficient use of Resources
Product Specification
| Material | GI Structure with Mono Net |
| Color | Black / Green / Red / White |
| Width | 40 Meter |
| Length | 100 Meter |
| Thickness | 90 Gsm / 100 Gsm / 120 Gsm |
| Shading | 50% To 90% |
| Usage/Application | Agriculture |
| Brand | Shri Ji |
| Durability | 2-3 Year |
| Application | Vegetable Grow |
| Minimum Order Quantity | 4000 Sqm. |
Additional Information
| Item Code | SJI-0145 |
| Delivery Time | Same Day |
| Port of Dispatch | Jodhpur |
| Production Capacity | 50,000 Sqm. |
| Packaging Details | Large Bag’s |
| Packing Qty | 1 Bag |
| Payment Terms | Advance |
| Payment Mode | RTGS / NEFT / IMPS |
Construction Materials for Shade Net Houses:
Shade Net Houses require specific construction materials to ensure durability, stability, and proper functioning. Here are some key materials commonly used in the construction of Shade Net Houses:
-
Framework Materials:
- Galvanized steel pipes: Provide strength and durability.
- Aluminum profiles: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant.
- Bamboo poles: Cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative.
-
Shade Netting Materials:
- High-density polyethylene (HDPE) nets: Durable, UV-resistant, and available in various shade percentages.
- Knitted polypropylene (PP) nets: Offers good ventilation and light transmission.
-
Anchoring and Support Materials:
- Concrete or steel foundation posts: Ensure stability and prevent shifting.
- Wire ropes and cables: Used for bracing and securing the structure.
- Ground stakes or anchor plates: Help secure the structure to the ground.
-
Fastening and Joining Materials:
- Galvanized steel clamps or brackets: Used to connect and secure framework components.
- Nylon zip ties: Provide quick and easy fastening of shade netting to the framework.
- Metal screws or bolts: Used for joining different structural elements.
-
Additional Materials:
- Plastic or metal connectors: Aid in joining and reinforcing frame sections.
- Anti-drip and anti-fogging agents: Reduce condensation inside the structure.
- Ventilation fans and screens: Enhance air circulation and control temperature.
It’s important to note that the specific choice of construction materials may vary based on local climate, budget, and intended use of the Shade Net House.
Design Considerations for Shade Net Houses:
Designing an efficient and functional Shade Net House requires careful consideration of various factors. Here are some key design considerations to keep in mind:
-
Location and Orientation:
- Select a suitable site with proper sunlight exposure and access to water sources.
- Orient the structure to optimize significantly sunlight penetration and minimize shading from nearby obstacles.
-
Size and Layout:
- Determine the required size of the Shade Net House based on the intended crops and production goals.
- Plan the layout to efficiently efficiently accommodate walkways, irrigation systems, and storage areas.
-
Structure and Framework:
- Choose a sturdy framework material (e.g., galvanized steel, aluminum) capable of withstanding wind loads and supporting the shade netting.
- Incorporate appropriate roof pitch and truss design to shed water and prevent accumulation.
-
Shade Netting Selection:
- Consider the desired shade percentage based on the specific crop requirements and local climate conditions.
- Ensure the shade netting material (e.g., HDPE, PP) is durable, significantly UV-resistant, and allows sufficient air circulation.
-
Ventilation and Temperature Control:
- Incorporate proper ventilation systems such as side vents, ridge vents, or exhaust fans to regulate temperature and humidity levels.
- Install shade nets with open-weave designs to facilitate natural airflow.
-
Irrigation and Drainage:
- Design an efficient irrigation system with drip lines or sprinklers to deliver water directly to the plant roots.
- Incorporate appropriate drainage systems to prevent significantly waterlogging and facilitate excess water removal.
-
Crop Support Structures:
- Determine the need for trellises, support frames, or hanging systems to facilitate vertical growth and optimize space utilization.
- Consider the weight-bearing capacity of the structure and select suitable materials for supporting crops.
-
Pest and Disease Management:
- Incorporate insect-proof screens or nets on openings to prevent pest intrusion.
- Plan for easy access and integration of pest control measures such as sticky traps or biological controls.
-
Accessibility and Ergonomics:
- Ensure adequate space for workers to move comfortably within the Shade Net House.
- Consider the structure’s height, door placements, and pathways to facilitate easy movement and harvesting.
Considering these design aspects, you can create a well-designed Shade Net House that promotes optimal plant growth, certainly productivity, and ease of operations.
Types of Shade Net Materials Used in Shade Net Houses:
The choice of shade netting material is crucial in Shade Net House construction to regulate sunlight penetration and create an optimal growing environment. Here are certainly some commonly used shade net materials:
-
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Nets:
- Made from high-density polyethylene, a durable and UV-stabilized material.
- Available in different shade percentages, such as 30%, 50%, or 70%, to control light intensity.
- Offers excellent resistance to tearing, harsh weather conditions, and certainly prolonged exposure to sunlight.
- Allows air circulation and reduces wind speed, minimizing crop damage.
-
Knitted Polypropylene (PP) Nets:
- Constructed using polypropylene fibers woven in a knitted pattern.
- Provides good ventilation, light diffusion, and even shade distribution.
- Lightweight and easy to handle during installation.
- Resistant to rot, mildew, and UV degradation.
-
Aluminized Shade Nets:
- Consists of HDPE or PP nets with a reflective aluminum coating.
- It offers enhanced temperature regulation by reflecting a portion of the sunlight away from the crop.
- It helps maintain lower temperatures inside the Shade Net House, certainly particularly in hot climates.
- Reduces heat stress on plants and minimizes the risk of sunburn.
-
Woven Shade Cloth:
- Created by weaving individual strands of monofilament or tape into a mesh pattern.
- Provides shade levels ranging from 30% to 90% based on the tightness of the weave.
- Allows good air movement and light diffusion.
- Generally more economical compared to knitted nets.
-
Color-Specific Nets:
- Some shade net materials come in specific colors, such as black, white, or green.
- Black nets offer higher shade levels and are commonly used for light-sensitive crops.
- White nets provide moderate shading and reflect some light to minimize heat buildup.
- Green nets blend well with the surroundings and offer a balanced level of shading.
-
Monofilament Shade Nets:
- Constructed with individual thick filaments, providing higher strength and durability.
- Offers improved light transmission and reduced shadow patterns.
- Suitable for crops requiring more direct sunlight and where high wind speeds are a concern.
In addition, It’s important to consider the desired shade level, light transmission, durability, and specific crop requirements when selecting the appropriate shade net material for a Shade Net House.
Maintenance and Upkeep of Shade Net Houses:
Regular maintenance and upkeep are essential to ensure the longevity and optimal functioning of Shade Net Houses. Furthermore, Here are some key aspects to consider:
-
Inspecting the Shade Net House:
- Regularly inspect the structure for any signs of damage, such as tears, loose connections, or rusting of the framework.
- Check for sagging or unevenness in the shade netting and address it promptly.
-
Cleaning and Washing:
- Remove debris, leaves, and dirt from the shade netting, framework, and gutters.
- Wash the shade netting periodically with mild soap or specialized net cleaning products to remove dust, pollen, and other residues.
-
Repairing and Replacing Components:
- Repair or replace damaged or worn-out components, including framework elements, fasteners, and shade netting, as needed.
- Reinforce weak points like connectors and joints to maintain structural integrity.
-
Maintaining Irrigation Systems:
- Regularly check and clean irrigation lines, sprinklers, or drip emitters to ensure proper water distribution.
- Monitor water pressure and adjust as necessary to avoid over- or under-irrigation.
-
Pest and Disease Management:
- Implement preventive measures, such as installing insect screens and regularly inspecting for pest infestations.
- Follow integrated pest management practices and apply appropriate treatments or biological controls, if necessary.
-
Weed Control and Sanitation:
- Keep the area surrounding the Shade Net House free from weeds and vegetation that can harbor pests and diseases.
- Maintain cleanliness and sanitation within the structure to prevent the buildup of debris and disease vectors.
-
Monitoring Environmental Conditions:
- Regularly monitor temperature, humidity levels, and light conditions inside the Shade Net House.
- Adjust ventilation, shading, or cooling systems to maintain optimal growing conditions.
-
Seasonal Maintenance:
- Prepare the Shade Net House for changing seasons, such as reinforcing it against strong winds or protecting it from heavy snow loads.
- Adjust shade netting or ventilation systems to accommodate seasonal variations in light and temperature.
-
Training and Pruning Plants:
- Prune and train plants to promote proper growth, air circulation, and light penetration within the Shade Net House.
- Remove diseased or damaged plant material promptly to prevent the spread of infections.
-
Documenting and Recording:
- Maintain a record of maintenance activities, repairs, and modifications made to the Shade Net House.
- Keep track of crop performance, pest and disease incidences, and any observations relevant to the structure’s functioning.
A regular maintenance routine and addressing issues promptly, you can maximize the lifespan of the Shade Net House and create an optimal environment for your crops.